Of the Following Which Best Describes the Sliding Filament Theory
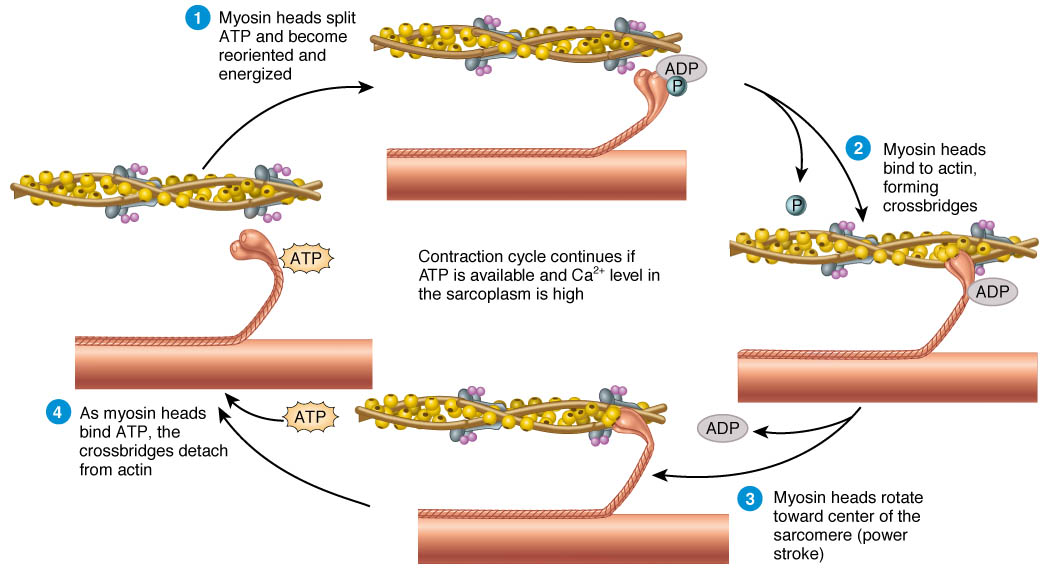
Describe the change that occurs in the myosin molecule between stage 1 attachment and stage 2. The myosin and actin can cross bridge.

Sliding Filament Model Of Contraction Biology For Majors Ii
4The binding of ATP to the cross bridge which results in the cross bridge disconnecting from actin.

. 2The binding of myosin to actin. Which of the following statements best describes the sliding filament mechanism of muscle contractiona. This theory was proposed by HE Huxley and J.
Which of the following statements best describes the sliding filament mechanism of muscle contraction. Which statement describes the sliding-filament theory. These filaments slide in and out between each other to form a muscle contraction hence called the sliding filament theory.
Which ONE of the following best describes the term sliding filament theory. The diagram above shows part a myofibril called a sarcomere. Biology 9th Edition Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 47 Problem 4U.
A filament of myosin during cross bridge cycling. Describe the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction. The Sliding Filament Theory is a description of the process of muscular contraction.
View the primary ISBN for. Muscle Histology Review. C To stimulate the detachment of the myosin heads from the.
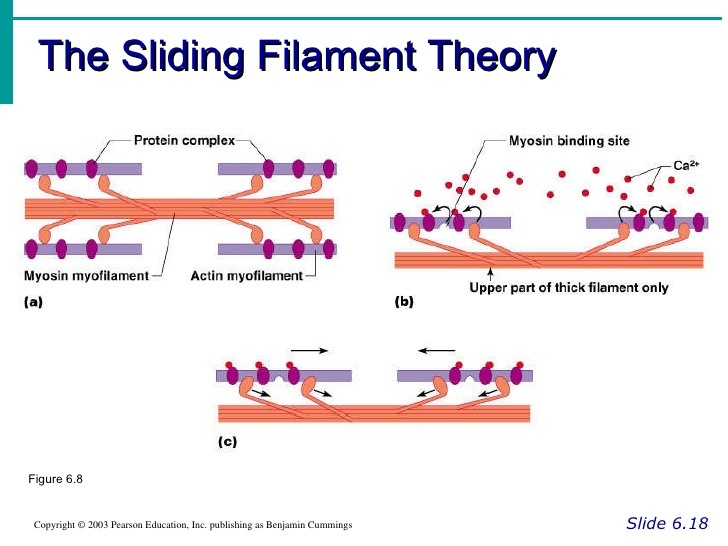
The calcium attaches to the troponin which removes tropomysosin from the myosin binding site on actin. At a very basic level each muscle fibre is made up of smaller fibres called myofibrils. One motor unit ОО An inactive actin filament The sliding filament theory O.
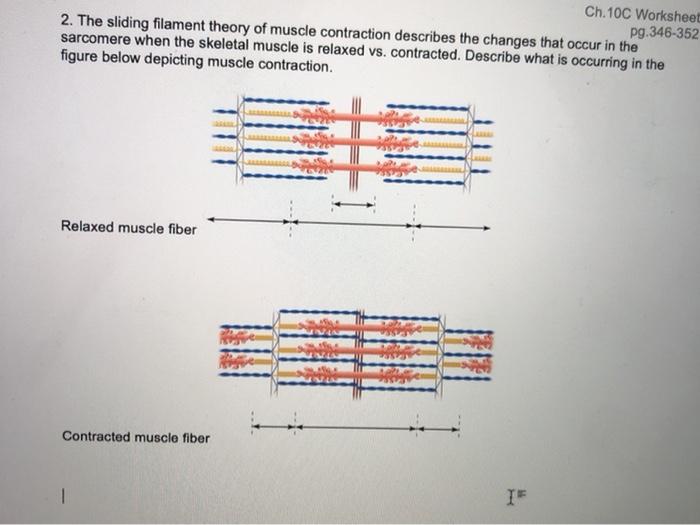
In the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction what is the primary role of calcium ions. Which of the following best describes the diagram. According to the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction the physical changes that occur in the sarcomere during contraction are a result of the thin filaments sliding past the thick filaments resulting in shortening of all the sarcomeres in a myofibril.
Actin and myosin filaments shorten and slide past each other. Science Anatomy and Physiology QA Library Which of the following best describes the diagram. These contain even smaller structures called actin and myosin filaments.
Actin and myosin filaments shorten and slide past. Actin and myosin filaments do not shorten but rather slide past each other. For a muscle to contract thick and thin filaments of sarcomeres do not shorten instead they slide by one another causing the sarcomere to shorten while the filaments remain the same length.
Which of the following best describes the diagram. 1 The release of acetylcholine along the motor neurons stimulating muscle contraction 2 Thick and thin filaments slide past one another to form muscle contractions 3 A neurotransmitter sends an impulse from one filament to the other enabling the muscle to lengthen thus creating. Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction.
It stimulates the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium ions. Muscles contract in order to move limbs or maintain a certain position or posture. Biology 9th Edition Textbook Solutions.
One motor unit An inactive actin filament The sliding filament theory. This theory describes the way a muscle cell contracts or shortens as a whole by the sliding of thin filaments over thick filaments and pulling the Z discs. According to the sliding filament theory the myosin thick filaments of muscle fibers slide past the actin thin filaments during muscle.
B To initiate the release of a molecule of ADP as the myosin heads pull the actin filament along. In 1954 two researchers Jean Hanson and Hugh Huxley from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology made a model for muscle tissue contraction which is known as the sliding filament theory. However for the muscle as a whole to contract the actin and myosin filaments must overlap causing the sarcomere to shorten.
5The hydrolysis of ATP which leads to re-energizing. This mechanism is explained by the sliding filament theory. 3The power stroke of the cross bridge that causes the sliding of the thin filaments.
Up to 24 cash back The Sliding Filament Theory How do muscle cells contract Model 1. Muscular contraction Is the shortening of myofibrils in response to nervous stimulation and during this actin filament slides over myosin filament and links with them resulting in. Impulse arrives at neuromuscular junction.
And 1 to put the following events in. Actin and myosin filaments do not shorten but rather slide past each otherb. A sarcomere in relaxed above and contracted below positions.
A filament of myosin during cross bridge cycling. The mechanism of muscle contraction is explained by sliding filament model. Be sure to use the terms actin and myosin in your answer.
1The influx of calcium triggering the exposure of the binding sites on actin. As they slide past each other actin filaments shorten but myosin filaments do not shorten. Sliding filament theory describes the muscle contraction theory.
The sliding filament theory explains the mechanism of muscle contraction based on muscle proteins that slide past each other to generate movement. A To provide the energy required to return the myosin heads back to their normal position. This process is triggered by the release of calcium ions in the presence of the proteins.
The sliding filament theory is a suggested mechanism of contraction of striated muscles actin and myosin filaments to be precise which overlap each other resulting in the shortening of the muscle fibre length. The arrangement of actin and myosin myofilament within a sarcomere is crucial in the mechanism of muscle contraction. Actin thin filaments combined with myosin thick filaments conduct cellular movements.
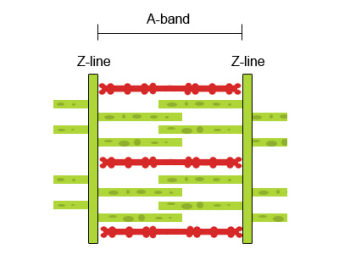
The striated pattern of skeletal muscle viewed under the microscope is created by the regular arrangement. The actin and myosin interact and the actin is pulled over the myosin shortening the sarcomere.
A Basic Look At How A Muscle Contracts

Muscle Contraction Sliding Filament Theory Teachpe Com
The Sliding Filament Theory Sfa Sk
Sliding Filament Theory Human Anatomy Quiz Quizizz

Sliding Filament Theory Muscle Contraction 6 Steps D Diagram Quizlet
Solved Ch 10c Worksheet Pg 346 352 2 The Sliding Filament Chegg Com

Sliding Filament Theory Biology Quizizz

Illustration Of The Sliding Filament Hypothesis It Is Seen That When Download Scientific Diagram

Question 48 1 Point Which Of The Following Best Chegg Com

Sliding Filament Theory Diagram To Label Diagram Quizlet

Lesson Explainer Muscle Contraction Nagwa

38 4c Sliding Filament Model Of Contraction Biology Libretexts

Thefatstudent 9 32pm Sliding Filament Theory Of Muscle Contraction Poster To Go On My Revision Wall A Level Biology Biology Revision How To Study Anatomy
Solved Sliding Filament Theory Model The Theory Of How Muscle Contracts Is The Sliding Filament Theory The Contraction Of A Muscle Occurs As The Course Hero

Sliding Filament Theory Of Muscle Contraction Explained Youtube

Sliding Filament Mechanism Of Muscle Contraction Anatomy And Physiology Study Notes Nursing Study
According To The Sliding Filament Theory What Happens As A Muscle Shortens Quora

Sliding Filament Theory Of Muscle Contraction In Which Actin Filaments Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment